Pacific International Liquor Revenue, Growth & Competitor Profile
Last updated:
Company Awards
Brain Power (IP)

Company Profile & Annual Report for Pacific International Liquor
Access the complete profile.Pacific International Liquor Fast Facts
| Revenue | $1 - $10 million See Exact Annual Revenue |
|---|---|
| Employees | 10 - 100Exact Company Size |
| Primary Industry | 4453 Liquor Stores |
| Address | 3090 E Via Mondo Rancho Dominguez, CA 90221 |
- What is the company's size? (Annual sales and employees)
- Pacific International Liquor's annual revenues are $1 - $10 million (see exact revenue data)
- What industry is the company in?
- Pacific International Liquor is classified as operating in the Liquor Stores industry, NAICS Code 4453.
Pacific International Liquor Annual Revenue and Growth Rate
| Pacific International Liquor | Revenue Est. ($ Million) | Growth Rate (%) | # Employees |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $1 - $10 million Details in Premium Report | ||
| 2022 | |||
| 2021 | |||
| 2020 | |||
| 2019 | |||
|
1-Year Growth Rate: 3-Year Growth Rate (CAGR): | 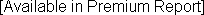 |
Note: Pacific International Liquor's revenues are gauged from an analysis of company filings.
Pacific International Liquor's Income Statement (based on Industry Averages)
| Pacific International Liquor P&L | $ Millions |
|---|---|
| Revenue (Sales) | 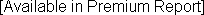 |
| Cost of Goods Sold | |
| Gross Profit | |
Operating Expenses | |
| Advertising | |
| Salaries and wages | |
| Other Operating Expenses | |
| Total Operating Expenses | |
| Operating Income | |
| EBITDA | |
| EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) | |
| Net Profit | |
Trademark Applications
Trademark applications show the products and services that Pacific International Liquor is developing and marketing. Pacific International Liquor doesn't have any recent trademark applications, indicating Pacific International Liquor is focusing on its existing business rather than expanding into new products and markets. Trademarks may include brand names, product names, logos and slogans.| Trademark | Date |
|---|---|
| TOBIN Sake | 12/01/2020 |
| LEO Sake; Wine; Distilled spirits; Liqueurs; Korean distilled spirits (Soju) | 09/15/2020 |
| KAWABA Beer | 01/28/2020 |
See all trademarks and details in the Full Report.
Market Share of Pacific International Liquor's Largest Competitors
A competitive analysis shows these companies are in the same general field as Pacific International Liquor, even though they may not compete head-to-head. These are the largest companies by revenue. However, they may not have the largest market share in this industry if they have diversified into other business lines. The "Competition" section of a business plan or investment memorandum would start by analyzing the information about these companies. Competitive advantage comes from offering better pricing or superior products/service.| Company | Headquarters | Revenue ($ MM) |
|---|---|---|
| RETAIL SERVICES & SYSTEMS | Bethesda, MD | 100 |
| SPECS FAMILY PARTNERS | Houston, TX | 36 |
| BEVERAGES & MORE | Concord, CA | 29 |
| GOLD STANDARD ENTERPRISES | Niles, IL | 10 |
| ABC FINE WINE & SPIRITS | Orlando, FL | 10 |
| TWIN LIQUORS | Austin, TX | 8 |
| YANKEE SPIRITS | Sturbridge, MA | 4 |
| CHESTERFIELD VENTURES LLC DBA HAMLIN PUB OF CHESTERFIELD | Chesterfield, MI | 4 |
| LIQUOR MANAGEMENT | Doral, FL | 3 |
Nearby Competitors
These companies are similar in business line and location to Pacific International Liquor. While some companies compete with neighboring businesses for customers, other companies may compete to attract skilled employees.| Company | Headquarters | Revenue ($ MM) |
|---|---|---|
| SOUTHWEST WINE & SPIRITS | Culver City, CA | 100 |
| STANLEY'S WET GOODS | Los Angeles, CA | 10 |
| RCGF&B | Beverly Hills, CA | 5 |
| PACIFIC INTERNATIONAL LIQUOR | Rancho Dominguez, CA | 4 |
| BLUEBIRD BUSINESS | Hawthorne, CA | 4 |
Future Competition: Pacific International Liquor's Fastest Growing Competitors
These companies are in the same general field as Pacific International Liquor and are rapidly expanding. Companies may grow organically or through acquisition. In some cases apparently high growth rates may be caused by data that weren't available in previous years.| Company | Revenue ($ MM) |
|---|---|
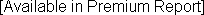 | |

 My Watch List
My Watch List